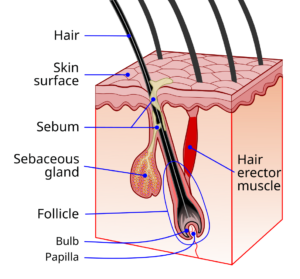
Hair loss, medically known as alopecia, is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It can occur in various forms, ranging from a slight thinning of the hair to complete baldness. This article delves into the different aspects of hair loss disease, its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options.
Causes of Hair Loss Disease
There are numerous factors that can contribute to hair loss. Understanding these causes is crucial in determining the most effective treatment approach.
Genetics
Genetics plays a significant role in hair loss. Androgenetic alopecia, also known as male-pattern baldness or female-pattern baldness, is the most common type of hair loss. It usually occurs gradually and in predictable patterns, such as receding hairline and bald spots in men, and thinning hair in women.
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal changes and imbalances can also cause temporary or permanent hair loss. This can be due to pregnancy, childbirth, menopause, or thyroid problems.
Medical Conditions
Certain diseases can lead to hair loss, including alopecia areata, which involves patchy hair loss, scalp infections such as ringworm, and a hair-pulling disorder called trichotillomania.
Symptoms of Hair Loss Disease
The symptoms of hair loss can vary greatly depending on its cause. Here are some common signs and symptoms.
Gradual Thinning on Top of Head
This is the most common type of hair loss, affecting both men and women as they age. In men, hair often begins to recede from the forehead in a line that resembles the letter M. Women typically retain the hairline on the forehead but have a broadening of the part in their hair.
Patchy or Circular Bald Spots
Some people experience smooth, coin-sized bald spots. This type of hair loss usually affects just the scalp, but it sometimes also occurs in beards or eyebrows. In some cases, your skin may become itchy or painful before the hair falls out.
Diagnosis of Hair Loss Disease
Diagnosing hair loss often involves a thorough examination of your hair and scalp, and a review of your medical history. Here are some common diagnostic methods.
Physical Examination
The doctor will examine your scalp to determine the pattern of hair loss. They may also pull out a few hairs to assess the strength of your hair.
Blood Tests
Blood tests can help uncover medical conditions related to hair loss, such as thyroid disease.
Scalp Biopsy
In some cases, a small sample of skin from the scalp may be taken to determine whether an infection is causing hair loss.
Treatment Options for Hair Loss Disease
There are several treatment options available for hair loss, depending on the cause. Here are some common treatments.
Medications
Medications such as minoxidil (Rogaine) and finasteride (Propecia) are commonly used in the treatment of hair loss. Minoxidil is a topical medication that is applied to the scalp, while finasteride is a prescription pill.
Surgical Procedures
If medications aren’t effective, a hair transplant or scalp reduction might be an option. These procedures can be expensive and carry risks, so they are usually considered as a last resort.
EsteNove is dedicated to offering personalized care to individuals seeking hair transplantation, boasting a team of skilled doctors and cutting-edge facilities. Whether you’re grappling with various forms of hair loss, EsteNove is here to assist you in rejuvenating your hair and regaining your self-assurance.
Lifestyle Changes
Healthy lifestyle habits, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, can help improve hair health and slow down hair loss.
Hair loss disease is a complex condition with various causes and symptoms. While it can be distressing, understanding the condition and seeking appropriate treatment can help manage the symptoms and improve the quality of life.